DATABASE NORMALIZATION
What is Normalization?
- NORMALIZATION is a database design technique that reduces data redundancy and eliminates undesirable characteristics like Insertion, Update and Deletion Anomalies.
- Normalization rules divides larger tables into smaller tables and links them using relationships.
- The purpose of Normalization in SQL is to eliminate redundant (repetitive) data and ensure data is stored logically.
Database Normal Forms
Here is a list of Normal Forms
- 1NF (First Normal Form)
- 2NF (Second Normal Form)
- 3NF (Third Normal Form)
- BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form)
- 4NF (Fourth Normal Form)
- 5NF (Fifth Normal Form)
- 6NF (Sixth Normal Form)
Note: The Theory of Data Normalization in SQL is still being developed further. For example, there are discussions even on 6th Normal Form. However, in most practical applications, normalization achieves its best in 3rd Normal Form. The evolution of Normalization theories is illustrated below-
.png)
Database Normalization With Examples
Database Normalization Example can be easily understood with the help of a case study. Assume, a video library maintains a database of movies rented out. Without any normalization, all information is stored in one table as shown below.

Here you see Movies Rented column has multiple values. Now let’s move into 1st Normal Forms:
1NF (First Normal Form) Rules
- Each table cell should contain a single value.
- Each record needs to be unique.
1NF Example

What is a KEY?
A KEY is a value used to identify a record in a table uniquely. A KEY could be a single column or combination of multiple columns
What is a Primary Key?
A primary is a single column value used to identify a database record uniquely.
It has following attributes
- A primary key cannot be NULL
- A primary key value must be unique
- The primary key values should rarely be changed
- The primary key must be given a value when a new record is inserted.
What is Composite Key?
A composite key is a primary key composed of multiple columns used to identify a record uniquely
In our database, we have two people with the same name Robert Phil, but they live in different places.

Hence, we require both Full Name and Address to identify a record uniquely. That is a composite key.
2NF (Second Normal Form) Rules
- Rule 1- Be in 1NF
- Rule 2- Single Column Primary Key
It is clear that we can’t move forward to make our simple database in 2nd Normalization form unless we partition the table above.


We have divided our 1NF table into two tables viz. Table 1 and Table2. Table 1 contains member information. Table 2 contains information on movies rented.
Database - Foreign Key
In Table 2, Membership_ID is the Foreign Key

Foreign Key references the primary key of another Table! It helps connect your Tables
- A foreign key can have a different name from its primary key
- It ensures rows in one table have corresponding rows in another
- Unlike the Primary key, they do not have to be unique. Most often they aren’t
- Foreign keys can be null even though primary keys can not

Why do you need a foreign key?
Suppose, a novice inserts a record in Table B such as
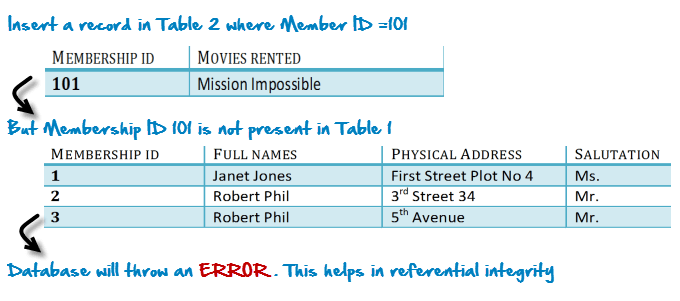
3NF (Third Normal Form) Rules
- Rule 1- Be in 2NF
- Rule 2- Has no transitive functional dependencies
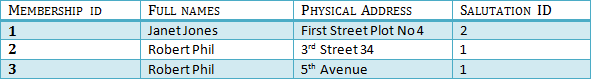

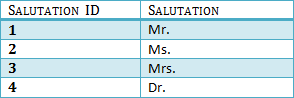
We have again divided our tables and created a new table which stores Salutations.
There are no transitive functional dependencies, and hence our table is in 3NF
In Table 3 Salutation ID is primary key, and in Table 1 Salutation ID is foreign to primary key in Table 3